Materiality Issues
Materiality Issues
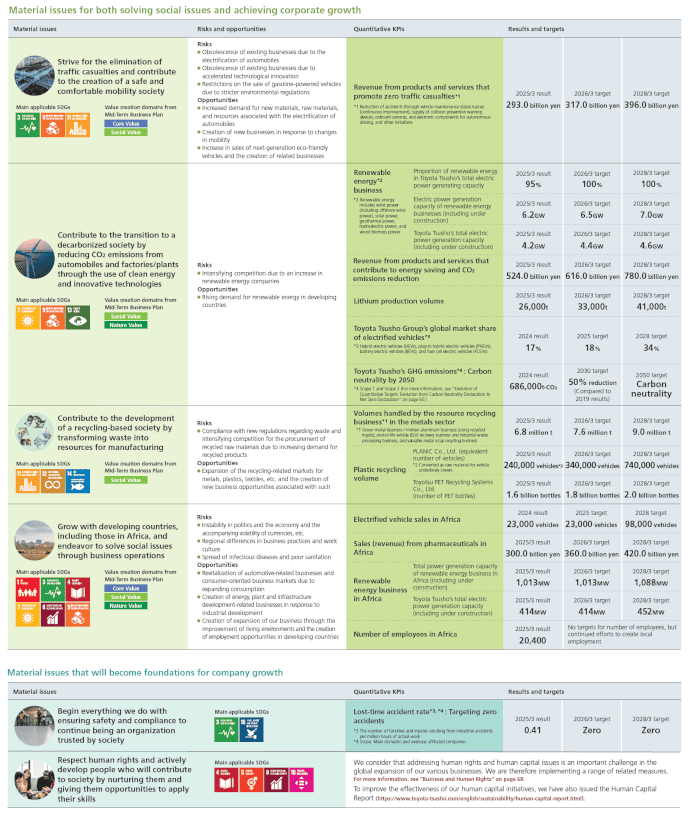
Toyota Tsusho has identified material issues (materiality) for realizing a sustainable society. For these materiality issues, we set both quantitative and qualitative KPIs (key performance indicators) and promote concrete initiatives by continuously monitoring progress.
When setting KPIs, we held repeated discussions with each division, including the CEOs of the sales divisions, to ensure that perspectives on materiality and the SDGs were reflected in divisional policies. In addition, at the Sustainability Committee, we exchanged views with senior management and outside directors to clarify the Company's direction and set targets for each symbolic theme.
Materiality is not fixed; each year we review the need for revisions in light of international trends, social needs, and changes in the environment surrounding the Toyota Tsusho Group. Likewise, KPIs are also updated as appropriate following discussions at the Sustainability Committee.
We incorporated into our employee evaluation indicators "contribution to the community, society, and the future" to encourage individual employees to take action with an awareness of the need to solve social issues. Training on sustainability and material issues is also conducted annually for new employees, including mid-career hires, to inform them of the importance.
We also designate every October as "Compliance Month," during which we disseminate messages from executives and hold lectures by external speakers, as well as various training programs on preventing misconduct, safety and compliance, the environment, sustainability, and human rights, to promote understanding and embed these concepts across the Company.

Process of Identifying Materiality Issues

1. Issue Identification

- We referred to guidelines such as CSR and ESG guidelines (GRI Standards, ISO 26000, United Nations Global Compact, FTSE, and MSCI) and the standards of Toyota Environmental Challenge 2050, focusing on the 17 goals and 169 targets of the SDGs, which are considered to comprehensively cover global social issues. From these, we identified and organized social issues that affect the company.
- We checked that these organized social issues aligned with our corporate philosophy, behavioral guidelines, Global Vision, and Mid-term Business Plan, and identified 43 social issues.
2. Prioritize Issues with Stakeholders
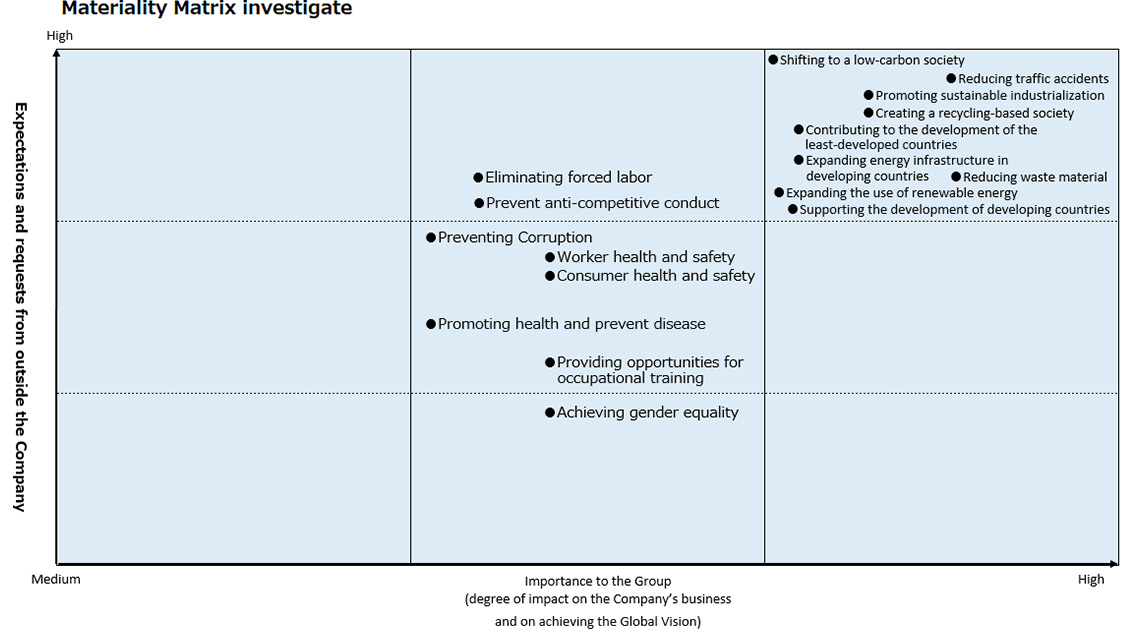
Through questionnaires and dialogue with stakeholders both inside and outside Toyota Tsusho regarding the identified 43 social issues, we prioritized expectations and requests for the company, as well as the importance of these social issues to the company, and created a Materiality matrix.
Stakeholders
- Internal: Interviews with individual sales divisions, and questionnaires administered to all company employees, CSR staff in Japanese-affiliated companies, and overseas staff
- External: Interviews with Japanese institutional investors, and questionnaires administered to general investors
Narrowing Down
Using a Materiality matrix, we created a Materiality proposal, focusing on social issues with a high level of importance inside and outside the company. While we are also addressing items that were not included in the proposal, those established as our material issues are items that we have identified as being the most important for the Toyota Tsusho.
3. Validation
The suitability of the identification process and the proposed material issues was confirmed.
Discussion Participants
- Discussion among management and division CEOs (current sales division CEOs)
- Individual interviews with outside members of the Board
Main Opinions from Participants
- It is noteworthy that the materialities are prepared after conducting a well-established process.
- This is no longer a time in which countries and governments can accomplish whatever they want on their own. It is necessary for society to change, and the Company needs to be aware of changing its systems and programs. It is necessary to refer to the knowledge of NGOs, NPOs, and other organizations.
- When viewed from the perspective of the materialities, we need to start a discussion on businesses that will become contradictory, businesses that should be slowed down, and businesses that we should terminate in the future. I want to establish materialities that will lead to an image of a set of guidelines for the future.
- It is necessary to change employee awareness so that we can expand perspectives from the Company's existing method of creating business by focusing on resolving customer problems and shifting from social issues that are global problems to a concept of business creation. Accumulating "quick hits" in the form of successful experiences will likely generate a virtuous cycle.
- The more amicable the language the vaguer it becomes, and this can give the impression that ultimately nothing will be done. So we need to use sharp language and adopt innovations.
- For employees, if the individual topics are narrowed down too far, the next step is difficult. But, if they are too general, it is difficult to know what to do. It is necessary to organize topics in a way that makes it easy for employees, as they are the ones who are to act.
4. Identify Our Material Issues
Our material issues were approved following discussions by the CSR Committee* (currently, the Sustainability Committee) at meetings held at the end of March 2018. Our material issues were reported at a Board of Directors meeting.
*Members at the time of 2018
President & CEO, Executive Vice President, CSO, CFO, Sales Division CEO, etc.
Two outside directors also participated as advisors
5. Set KPIs
- KPIs were set in 2020 to track progress on the identified material issues.
- When setting the KPIs, numerous discussions were carried out with the sales divisions, including the division CEOs, to reflect the approaches for solving social issues in the policies of each sales division. Furthermore, the Sustainability Committee reflected the opinions of management and outside members of the Board in the KPIs.
- Quantitative/qualitative targets were set as an expression of the direction we should aim for.
6. Initiatives
- Materiality elements were reflected in the business strategies of each sales division.
- We established the specialized Task Force for Promoting Carbon Neutrality in April 2021 to accelerate efforts to address climate change. In April 2022, the Carbon Neutrality Promotion Department was formed.
7. Review of Progress and Contents
- At Sustainability Committee meetings, the sales division CEOs report on the progress made in their respective divisions.
- The material issues and KPIs are reviewed periodically and revised as appropriate, taking into consideration changes in Toyota Tsusho's business environment, international trends and needs, and issues that emerge during the plan-docheck-act (PDCA) cycle.
Review of KPIs
Materiality and Materiality KPIs are confirmed periodically by the Sustainability Committee to ensure their suitability in light of changes in the environment and are revised if necessary.
List of Quantitative KPIs
Emerging risks
Our company refers to ISO/TS 31050 (Risk Management - Guidelines for Emerging Risk Management to Enhance Resilience) in addressing emerging risks.
In line with our medium-term management plan, we are pursuing business expansion into regions such as the Global South. In doing so, we anticipate the following emerging risks:
Geopolitical Risks
There is a possibility of project suspension or increased withdrawal costs due to regime changes triggered by coups or civil wars, which may result in contract invalidation, freezing of infrastructure investments, and shifts in diplomatic policy.
As mitigation measures, we implement Business Continuity Planning (BCP) and diversify operational bases to reduce exposure to regional risks.
Social Risks
Rapid urbanization, expansion of slums, and widening social inequality may lead to deteriorating public safety and the emergence of protest movements, which can affect logistics, talent acquisition, and compliance operations.
To mitigate these risks, we promote the establishment of alternative logistics routes, conduct internal compliance training, and strengthen relationships with local communities.
These and other risks are comprehensively assessed and discussed within our Investment and Financing Committee and Investment and Financing Council, where decisions regarding business development are made.