Environmental Business
Toyota Tsusho Renewable Energy Businesses
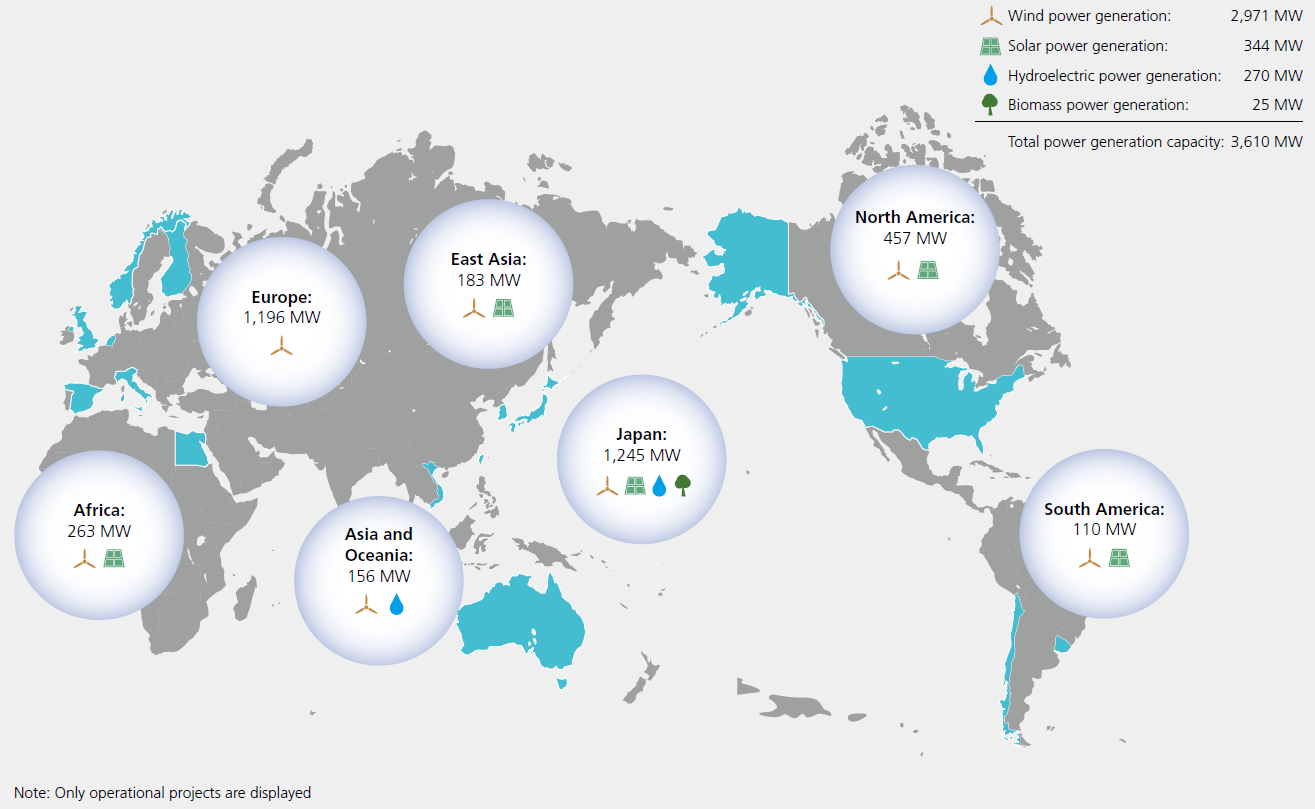
A Renewable Energy Business with a Total Capacity of More than 6GW
The SDGs are a collection of global goals that seek to realize a more sustainable future for all. In the electric power business, Toyota Tsusho is expanding its operations globally, focusing on various types of renewable energy power generation such as wind, solar, biomass, and hydroelectric power as businesses that contribute to resolving global environmental issues. As of March 2025, the Company owns more than 6 GW of renewable energy generation capacity across 17 countries worldwide and has grown to boast the largest generation capacity among wind and solar power operators in Japan.
In addition to its power generation business, the Company is also strengthening its initiatives in the storage battery business and the energy management business, working to promote the spread and expansion of renewable energy.
A History of More Than 30 Years in Renewable Energy Businesses
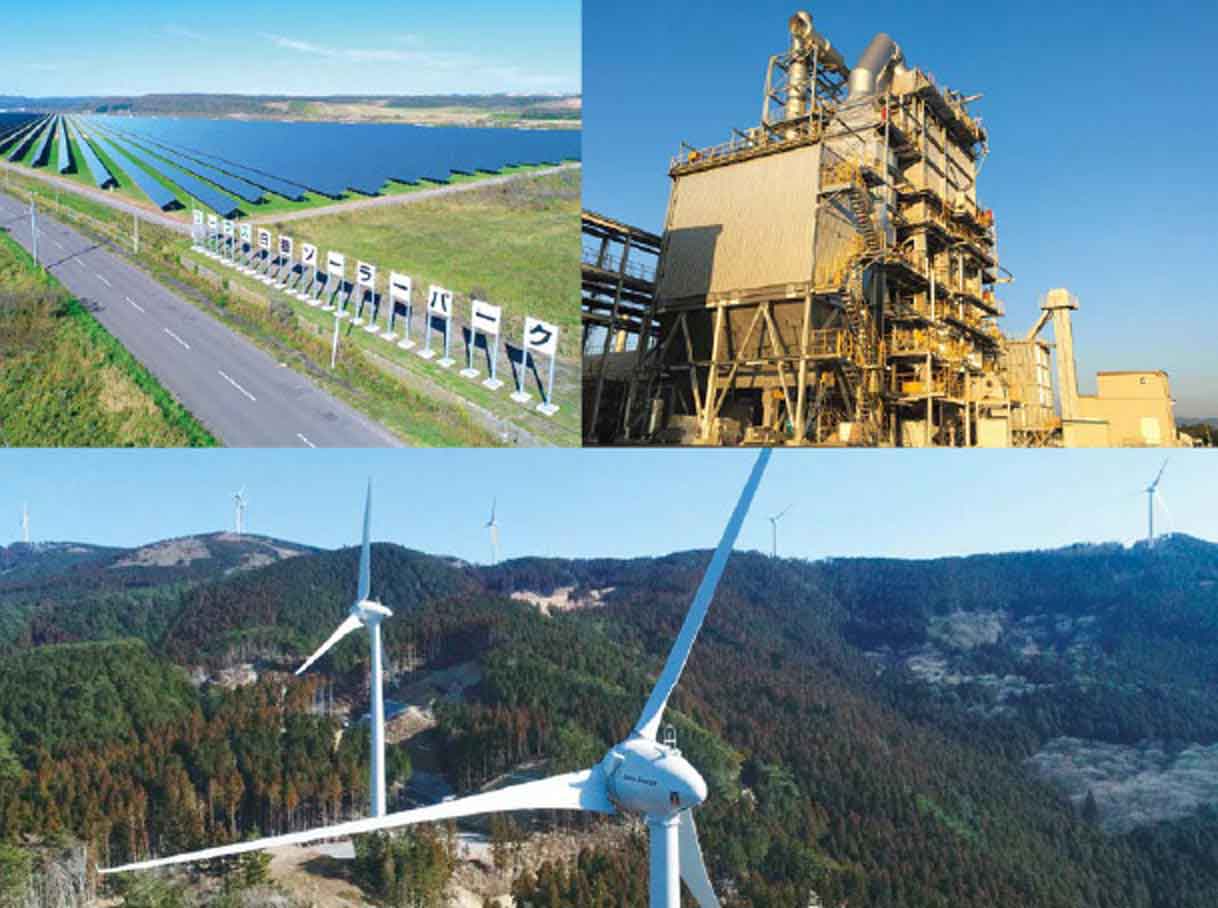

The Toyota Tsusho Group began its renewable energy business in 1987 with the Mojave Wind Power Plant in California, USA. This project, launched by the electric power division of Tomen Corporation (now Eurus Energy Holdings), started with a capacity of 5 MW. Since then, the Group has expanded its wind power business worldwide-beginning in the United Kingdom in Europe in 1993, South Korea in Asia in 2005, Uruguay in Central and South America in 2015, and Egypt in Africa in 2019.
In Africa, where the Company has particular strengths, the Gulf of Suez Wind Farm II in Egypt-boasting the region's largest generation capacity of 654 MW-commenced operation in August 2025. Together with the already-operational Gulf of Suez Wind Farm I, the total capacity has reached 916 MW, contributing to the expansion of renewable energy sources and economic development in the region.
In Japan as well, against the backdrop of the Kyoto Protocol signed in 1997 and expectations for the introduction of wind power utilizing Japan's abundant wind resources, the Company launched the nation's first large-scale wind power project in Tomamae Town, Hokkaido in 1999. Since then, it has continued to operate wind farms in areas with favorable wind conditions across the country, growing into Japan's leading wind power operator in terms of scale.
One distinctive initiative of Eurus Energy is its integrated generation, storage, and transmission business in the northern Hokkaido region.
Although the northern Hokkaido region is well-suited for wind power generation, the introduction and expansion of wind power had been hampered by a weak transmission network. To overcome this challenge, Eurus Energy established the North Hokkaido Wind Energy Transmission Corporation as a new company dedicated to transmission operations. With government support, the company developed a large-scale transmission network stretching approximately 78 km, along with one of the world's largest storage batteries with a capacity of 240 MW/720 MWh. As a result, more than 500 MW of wind power plants, including Eurus Energy's 450 MW facilities, can now be interconnected, enabling the region's abundant wind resources to be fully utilized.
The Group is also actively expanding its solar power generation business, beginning with Eurus Energy's business in South Korea in 2008 and subsequently promoting projects in countries around the world. The Group owns more than 1 GW of power generation capacity, including the solar power generation business of Terras Energy (formerly SB Energy), which became a subsidiary of Toyota Tsusho in 2023.
In April 2025, Eurus Energy and Terras Energy were integrated to further expand and strengthen the Group's renewable energy business.
Future Outlook for the Renewable Energy Sector Beyond 2030
In addition to further expanding its power generation business, the Toyota Tsusho Group has also begun initiatives in the energy management business and the storage battery business to ensure the stable delivery of renewable energy to customers going forward.
One specific initiative is the energy management business "ReEra." ReEra is a system that integrates and controls renewable energy and storage batteries. It "aggregates" renewable energy from across the nation using AI-powered demand and supply forecast, "regulates" it through optimal control of battery charging and discharging, and "delivers" renewable energy tailored to customer and market needs. By expanding and strengthening this value chain that delivers renewable energy-generated electricity seamlessly to customers, we contribute to more efficient use of renewable energy and to further promoting its adoption.
The Toyota Tsusho Group will continue to leverage the expertise it has cultivated in renewable energy to work toward realizing a sustainable energy society and resolving global environmental issues.
Other Environmental Business
Contributing to the Stable Supply of Battery Materials for Next-generation Eco-cars through the Production of Lithium
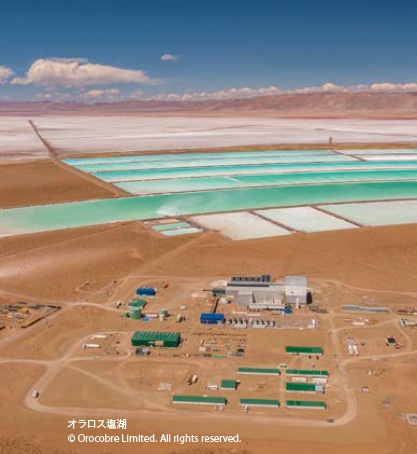

From the perspective of mobility, the widespread uptake of new energy vehicles is a key factor to reduce CO2 emissions and combating climate change. As a result, the production of lithium-ion batteries is increasing around the world. Toyota Tsusho takes part in the upstream domain of such to ensure a stable supply of lithium, which is one of rare resources.
In 2014, before new energy vehicles became popular, Toyota Tsusho commenced full-scale production of lithium carbonate, which is the raw material for rechargeable batteries. With lithium in short supply, as the result of a feasibility study, we chose Salar de Olaroz in Argentine Republic as the production base due to its having high-quality lithium resources, to be the production base.
Although companies from around the world vied to secure mining rights at the salt lake, the rights owner viewed Toyota Tsusho as a sustainable partner who had access to the targeted supply chain.
In 2012, Toyota Tsusho acquired a 25% interest of the production project at Salar de Olaroz. It acts as the exclusive sales agent for the lithium produced there.
In 2018, we established Toyotsu Lithium Corporation, the first dedicated lithium hydroxide manufacturing company in Japan.The company aims to manufacture and sell lithium hydroxide,which is a raw material for LiBs, and has built a manufacturing plant in Naraha-machi, Fukushima Prefecture,at which it started production in 2022.
By strengthening our alliances and by ensuring a stable supply of lithium resources, we intend to contribute to the realization of a sustainable society.
Anticipating the Future of Electrification

The popularization of electrified vehicles will bring with it unprecedented social issues, and the process of disposing of next-generation eco-cars will raise an as yet unanswered question how to process batteries for end-of-life vehicles (ELVs).
In the 1970s, the Toyota Tsusho Group launched a proper processing business for ELVs. Our initiatives in this field are accelerating globally, including in Thailand and India, and our business domain is expanding to cover iron, non-ferrous metals, precious metals, resins, and other materials. At Toyota Tsusho, we see applying such mechanisms to the lifecycles of next-generation eco-cars and responding to the needs of resource recovery as a new challenge.
Within our group, we have already commenced the recovery and proper processing of used nickel-metal hydride batteries and lithium ion batteries for hybrid vehicles (HVs). We are also focused on battery-tobattery resource recovery and expanding other battery utilization markets. By contributing to the comprehensive recycling of in-vehicle batteries and the establishment of sustainable automotive industry processes, we intend to link the Upstream (Arterial) businesses (production of battery materials, initiatives aimed at new materials and technologies, etc.) and Downstream (Venous) businesses (proper processing and recycling of automotive resources) of next-generation eco-cars and construct a kind of reverse supply chain.
At Toyota Tsusho, we believe it is our mission to support the popularization of next-generation eco-cars through such initiatives.
Materials with Lower CO2 Emissions than Petroleum-derived Products


In the materials sector, Toyota Tsusho and Toyota Tsusho Group company Toyotsu Chemiplas Corporation handle bio-polyethylene produced by Braskem, South America's largest chemicals manufacturer.
Bio-polyethylene is polyethylene that has been derived from plants, and in January 2011 Braskem became the first commercial producer of the material in the world. Toyota Tsusho has collaborated with Braskem from the development stages of the product to the present, and, as an official partner, it sells the product widely across Asia and Oceania.
Bio-polyethylene is made from sugarcane-derived ethanol.
In Brazil, this bioethanol is mainly consumed as a gasoline substitute. Sugarcane fields are primarily located in regions more than 2,000 kilometers away from the Amazon rainforest.
Also, because its raw material is a CO2-absorbing plant, even if a bio-polyethylene product is incinerated, based on the approach of carbon neutrality, it is expected to have a CO2 reduction effect of approximately 70% compared to petroleum-derived polyethylene.
Bio-polyethylene is already used in shampoo bottles, supermarket and convenience store plastic shopping bags, shopping baskets, municipal-designated garbage bags, PET drink bottle caps, and other food and drink containers.
Arterial and Venous Business Strategy Supports Monozukuri


We are seeing the expansion of a circular economy, which is characterized by, among other things, an increase in recycling opportunities for electronic devices including automobiles and rare metals, strenuous efforts to avoid using natural resources, viewing disposed of products, raw materials, and other materials as new resources, and recycling these materials to create products.
As far as the automotive industry is concerned, at Toyota Tsusho we call operations that pertain to production "arterial businesses," and those that pertain to post-production operations - such as scrap, waste, and automobile disposal - "venous businesses." Under our "Arterial and Venous Business Strategy," which we have prioritized, we view as resources the products, raw materials, and so on that previously were seen as waste, and we are promoting mechanisms and ecosystems for the recirculation of these resources. This is not limited to items (such as vehicles and parts) generated from mobility, but also extends broadly to production materials and waste such as plastic.
Aluminum is said to be the most effective replacement for iron to reduce vehicle weight. Since 1998, Toyota Tsusho has been supplying recycled secondary aluminum alloy ingots in a molten state, which has better CO2 emissions reduction effects, and is one of the world's top suppliers. The supply of molten recycled aluminum can generally be expected to have about a 98% CO2 emissions reduction effect compared to the use of new aluminum ingots refined using massive amounts of energy. As aluminum demand increases, we are developing technologies that can enhance the value of low-grade aluminum scrap and increase use rates, and we are creating smart factories that raise energy efficiency.
We also engage in the resin recycling business in Japan to contribute to recycling. Toyota Tsusho established PLANIC Co., Ltd., which is one of Japan's largest recycled plastic processing companies, in 2018, with operations commenced in 2022. PLANIC will use Japan's first advanced gravity sorting technology to use end-of-life plastic materials that are currently not effectively used from cars, consumer electronics, and other items to manufacture high-quality recycled plastic. In addition, we established Toyotsu PET Recycling Systems in 2020 to recycle waste PET bottles, with operations commenced in 2022. Moreover, we established Toyotsu Sorting Technology Corporation in 2023 , which has sorting and processing technology, to expand horizontal ecycling of aluminum sashes, with operations scheduled to commence in 2025.
