Toyota Tsusho to Conduct Practical Demonstration of Lane-level High-Accuracy Route Guidance System that Utilizes the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System "Michibiki"
-Adopted by JETRO as part of its "Project for Nurturing New Industries in ASEAN and Japan"-
- Chemicals & Electronics
2018-01-30
Toyota Tsusho Corporation (Toyota Tsusho) hereby announces that it will carry out a demonstration of a lane-class high-accuracy route guidance system that utilizes the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System, commonly known as "Michibiki*1," in Bangkok, Thailand. The proposal for the demonstration was accepted by the Japan External Trade Organization (JETRO) during the second round of applications for its "Project for Nurturing New Industries in ASEAN and Japan," and verification tests are scheduled to take place in March 2018.
1. Background of Demonstration Project
The Toyota Tsusho Group is providing of traffic congestion information that utilize GPS-based independent positioning in Thailand, which has one of the world’s highest volumes of traffic congestion. Position, time, and other data are gathered directly from taxis (probe cars) equipped with GPS receivers to generate traffic congestion information, which is then distributed via the TSquare Traffic information app and also provided to automakers. Through these systems, the Toyota Tsusho Group intends to contribute to the alleviation of congestion, a major societal problem in Thailand.
2. Purpose of Demonstration Project
The demonstration project utilizes “Michibiki” and “MADOCA*2” to gather lane-class probe information—which cannot be done using existing systems—and aims to realize the practical application of la lane-level high-accuracy route guidance system. Through this demonstration, the Toyota Tsusho Group seeks both to further contribute to alleviating traffic congestion in Thailand by improving its traffic information services, and to expand its business in fields that utilize high-accuracy positioning technologies.
3. Outline of Demonstration Project
The demonstration project equips probe cars that operate in urban Bangkok with high-accuracy multi-frequency multi-GNSS*3 receivers that can receive signals from Michibiki and correction data from MADOCA. Based on a combination of information from existing GPS systems and centimeter-class probe data from Michibiki and MADOCA, the project seeks to evaluate the technologies used by systems that generate lane-level high-accuracy traffic congestion information, and in systems that distribute high-accuracy route guidance; the project also aims to provide optimal route guidance.
|
Demonstration project period
|
December 2017–April 2018 |
|---|---|
|
Local verification test period
|
March 2018 (scheduled) |
|
Demonstration location
|
Bangkok, Thailand |
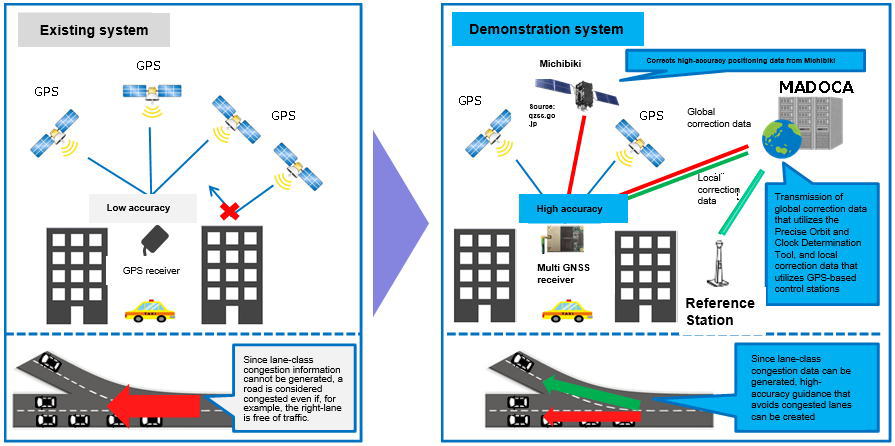
Michibiki is Japan’s satellite positioning system, and is expected to become a core basic technology for the “Connected Industries” concept framework proposed by the government.
The goals of this demonstration project are manifold: to contribute to the establishment of next-generation logistics technologies that utilize Michibiki; to improve innovation and productivity, as demanded by Thailand’s “Thailand 4.0” long-term vision; and to contribute to the realization of an economic society in which sustainable added-value can be generated through diversified trade.
Reference
The roles of the major groups participating in the demonstration project
| Group Name | Role | |
|---|---|---|
|
Toyota Tsusho Group
|
||
|
Toyota Tsusho Corporation
|
Project implementing company
|
|
|
TOYOTA TSUSHO NEXTY ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) CO., LTD.
|
Generation of lane-class congestion information and the establishment of a distribution system
|
|
|
The Japan Research Institute, Limited
|
Collation of advice and reports on the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System
|
|
|
ZENRIN DataCom Co., Ltd.
|
Development of high-accuracy route guidance navigation software
|
|
|
lobal Positioning Augmentation Service Corporation
|
Transmission of MADOCA correction data
|
|
|
agellan Systems Japan, Inc.
|
Provision of high-accuracy multi-frequency multi-GNSS receivers
|
|
|
hulalongkorn University (Thailand)
|
Provision of Local Reference Station
|
|
|
ichibiki Sora, Co., Ltd. (Thailand)
|
Verification of real-time positioning accuracy
|
|
*1 Michibiki:
Michibiki refers to the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), a Japanese satellite positioning system comprised primarily of quasi-zenith satellites. The system uses radio waves generated by the
satellites to calculate position information.
*2 MADOCA (Multi-GNSS Advanced Demonstration tool for Orbit and Clock Analysis):
Developed by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), MADOCA (Multi-GNSS Advanced Demonstration tool for Orbit and Clock Analysis) is a system that generates satellite signal correction
data. It is a precise orbit and clock determination tool that caters to multiple GNSSs*3.
*3 GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System):
GNSS stands for Global Navigation Satellite System, and is a collective term for global satellite positioning systems such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and QZSS.
The information in this release is current as of the date of announcement.
Please note that information may change after the date of announcement. Thank you in advance for your understanding.
